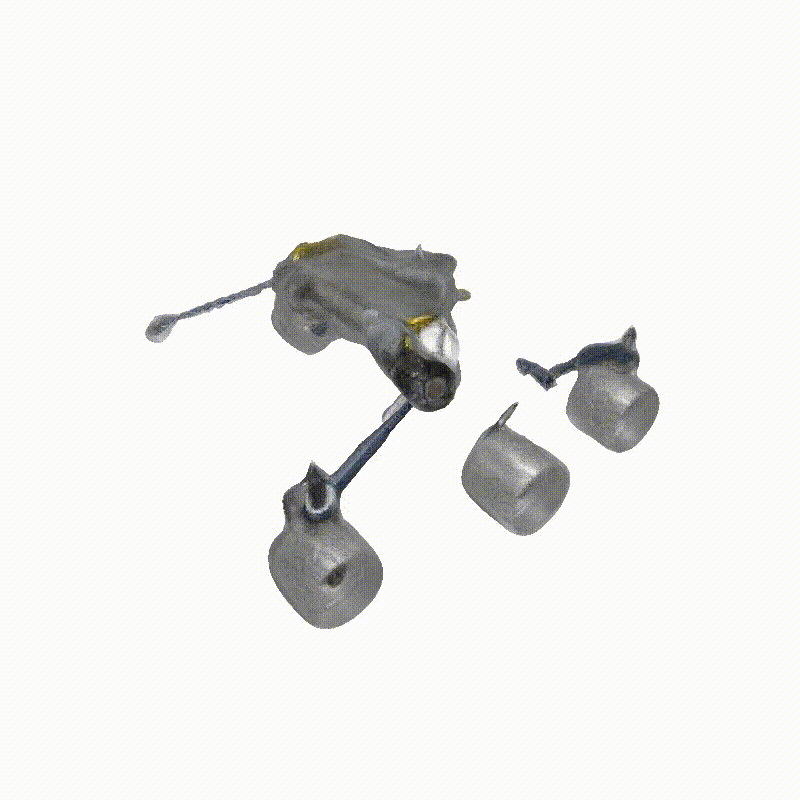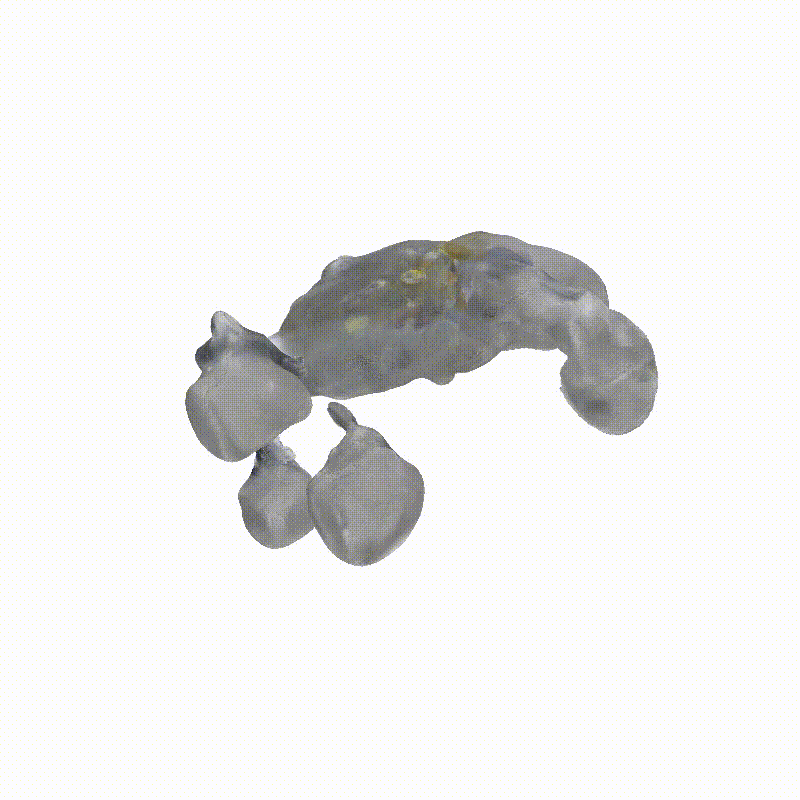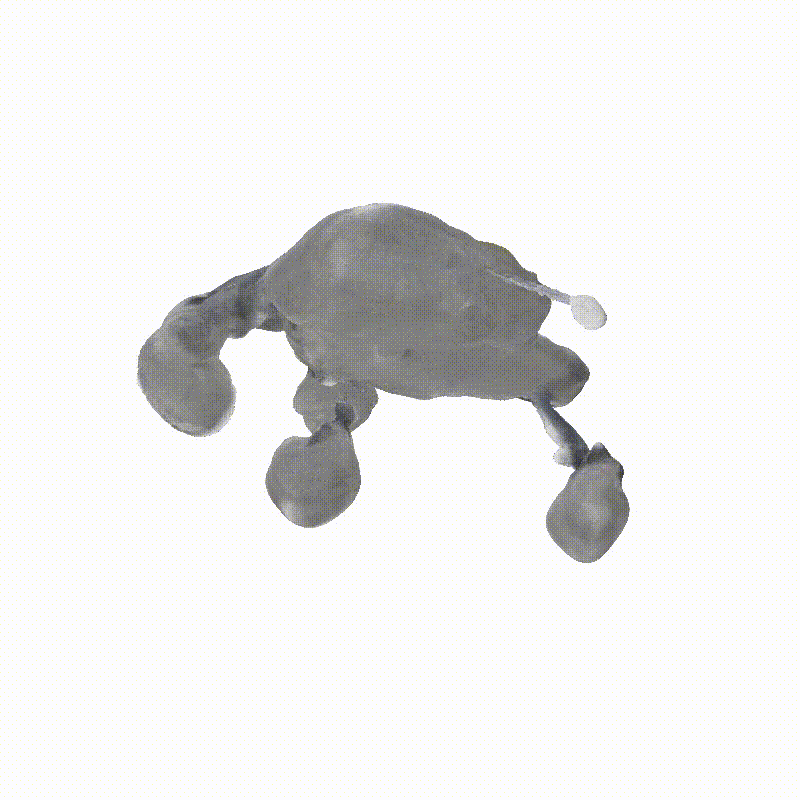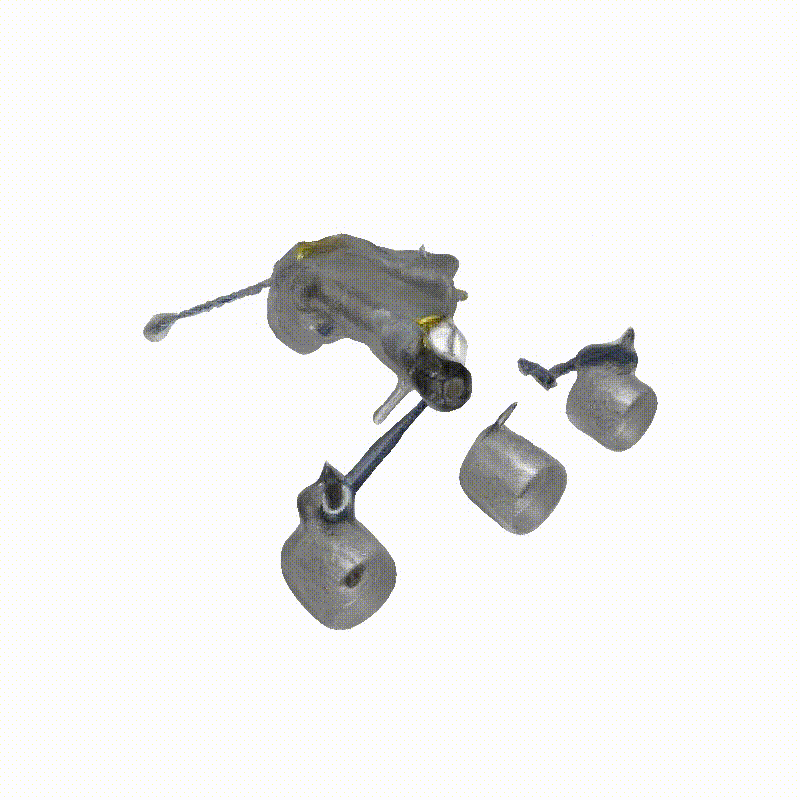
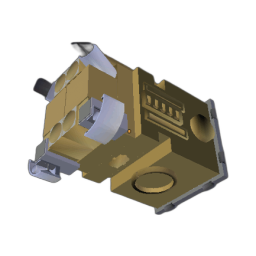
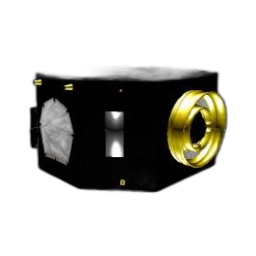
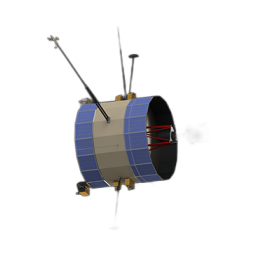
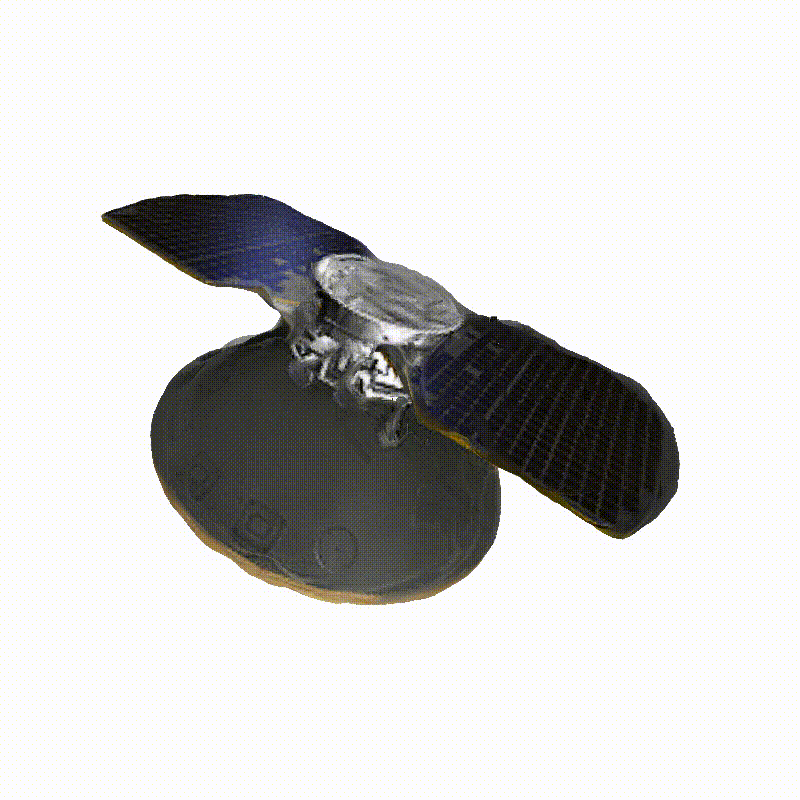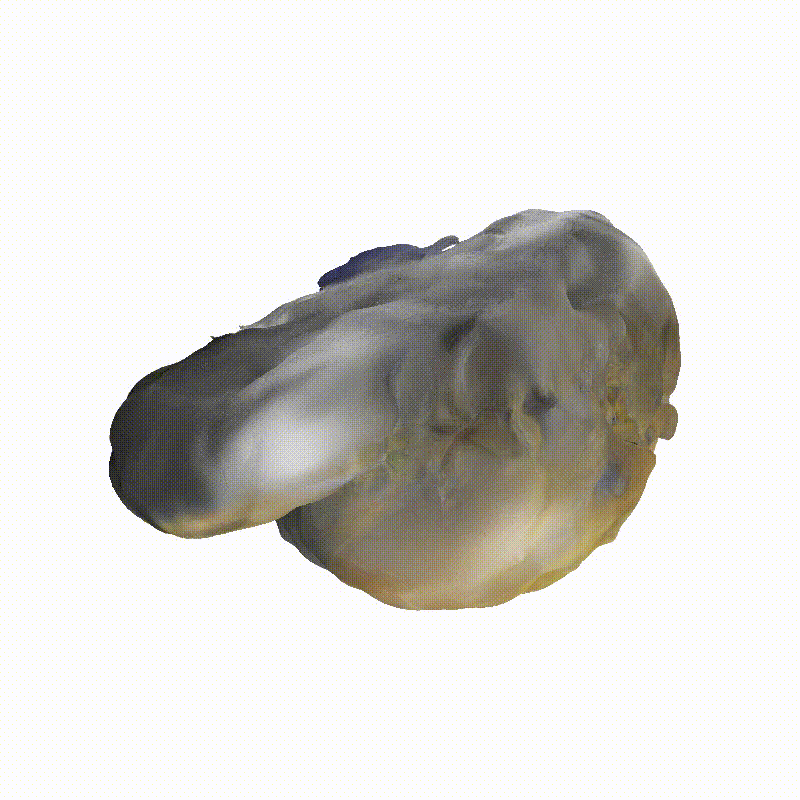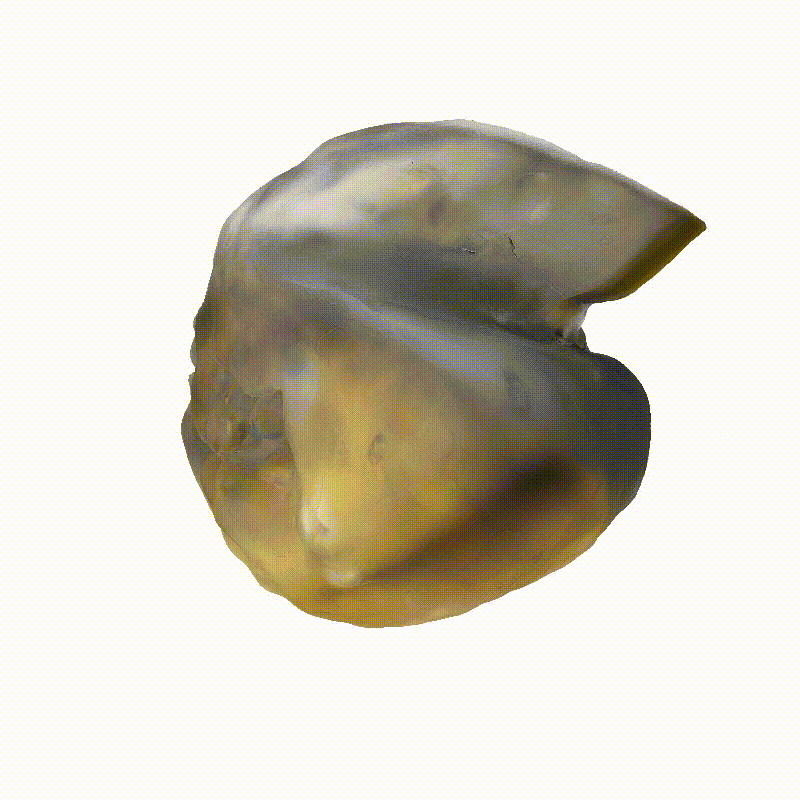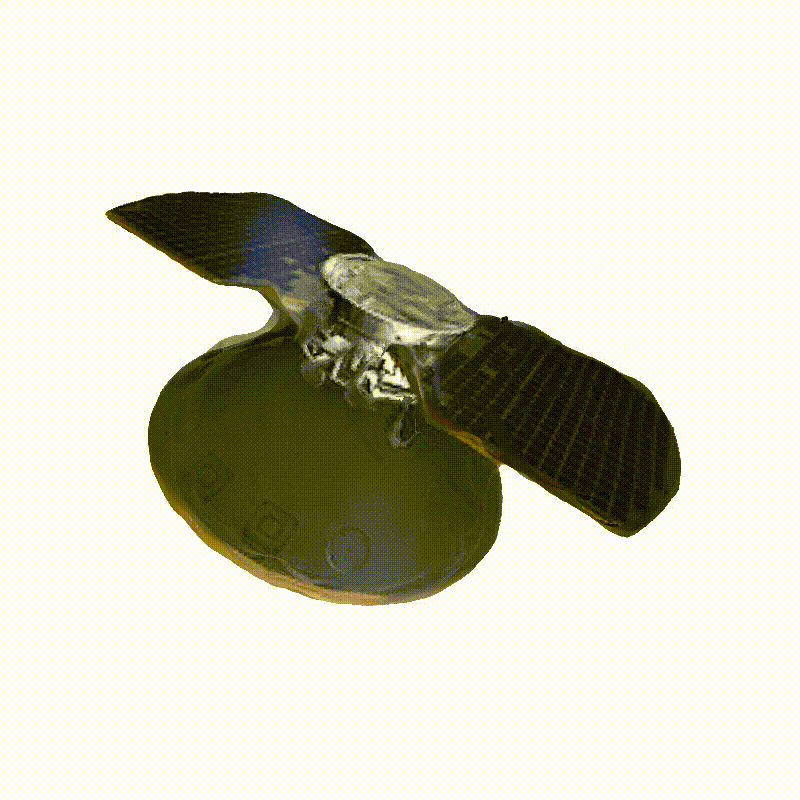
DreamSat: Towards a General 3D Model for Novel View Synthesis of Space Objects
Abstract
Novel view synthesis (NVS) enables the generation of new images of a scene or converting a set of 2D images into a comprehensive 3D model. In the context of Space Domain Awareness, since space is becoming increasingly congested, NVS can accurately map space objects and debris, improving the safety and efficiency of space operations. Similarly, in Rendezvous and Proximity Operations missions, 3D models can provide details about a target object's shape, size, and orientation, allowing for better planning and prediction of the target's behavior. In this work, we explore the generalization abilities of these reconstruction techniques, aiming to avoid the necessity of retraining for each new scene, by presenting a novel approach to 3D spacecraft reconstruction from single-view images by fine-tuning the Zero123 XL, a state-of-the-art single-view reconstruction model, on a high-quality dataset of 190 high-quality spacecraft models and integrating it into the DreamGaussian framework. For the implementation, we use spacecraft images obtained from the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), European Space Agency (ESA), and Synthetic Dataset for Satellites (SPE3R), allowing for generalization across common spacecraft 3D models. Our method addresses the lack of domain-specific 3D reconstruction tools in the space industry by leveraging state-of-the-art diffusion models and 3D Gaussian splatting techniques. We demonstrate significant improvements in reconstruction quality across multiple metrics, including CLIP score (+0.33%), PSNR (+2.53%), SSIM (+2.38%), and LPIPS (+0.16%) on a test set of 30 previously unseen spacecraft images. This approach maintains the efficiency of the DreamGaussian framework while enhancing the accuracy and detail of spacecraft reconstructions. Our work contributes to the advancement of 3D modeling capabilities in the aerospace industry, potentially reducing costs and improving efficiency in spacecraft design, mission planning, and virtual simulations.
Input

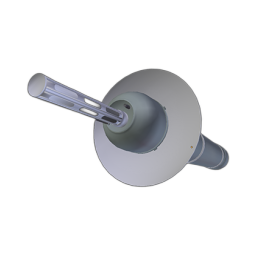
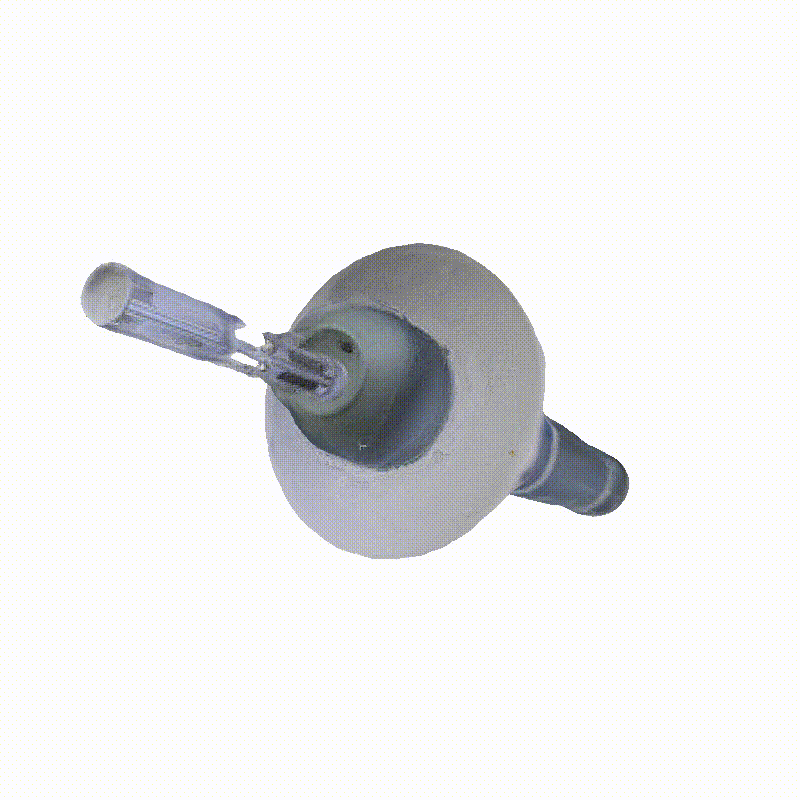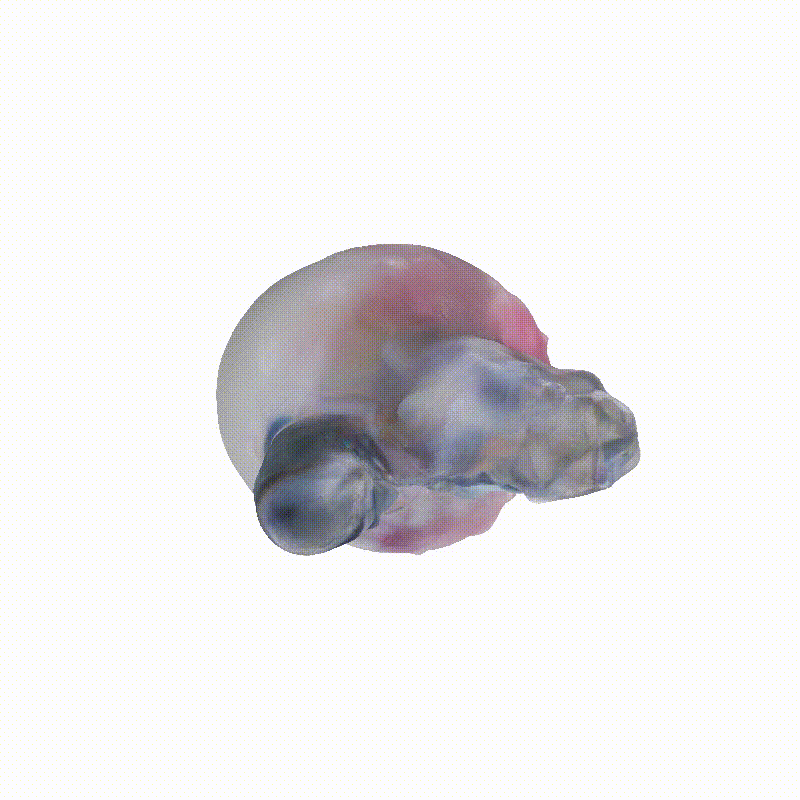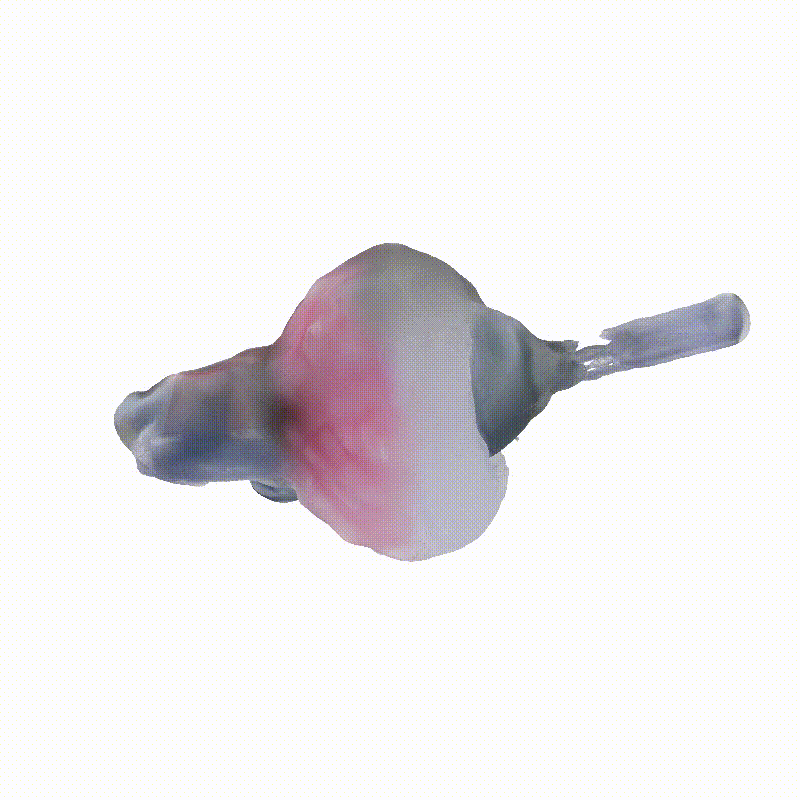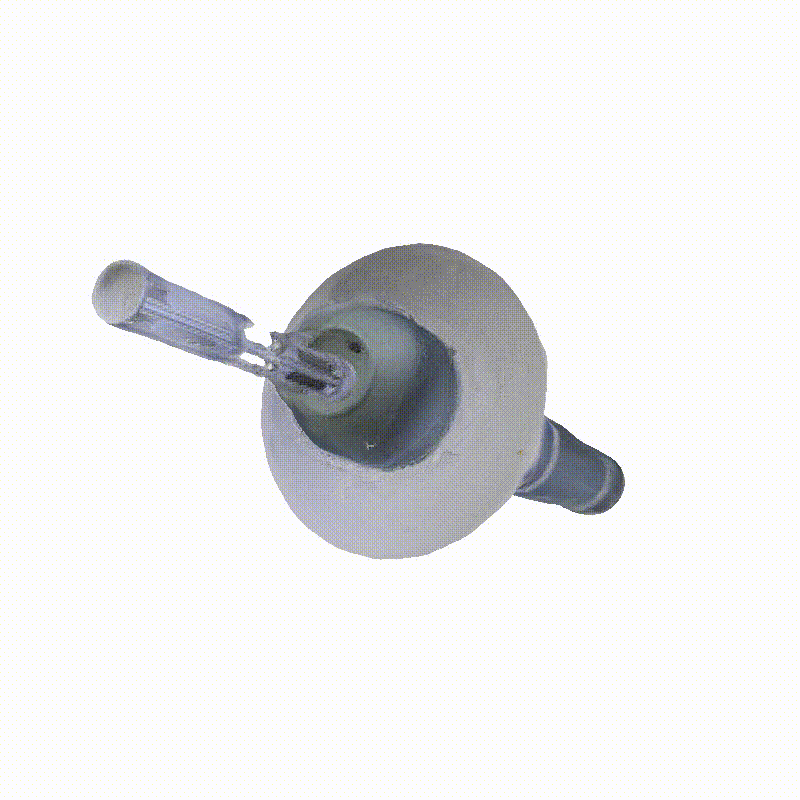
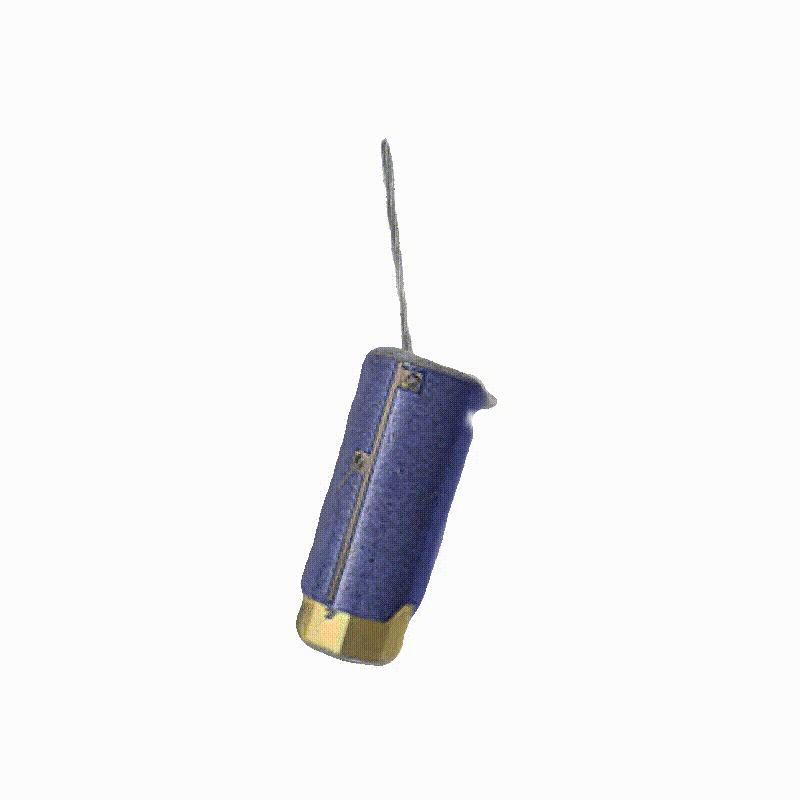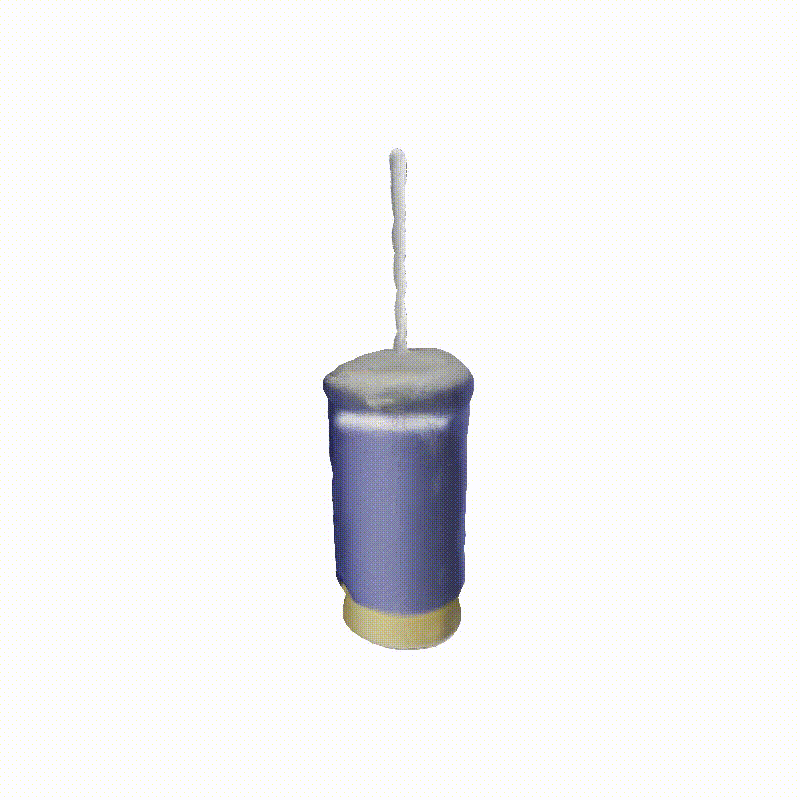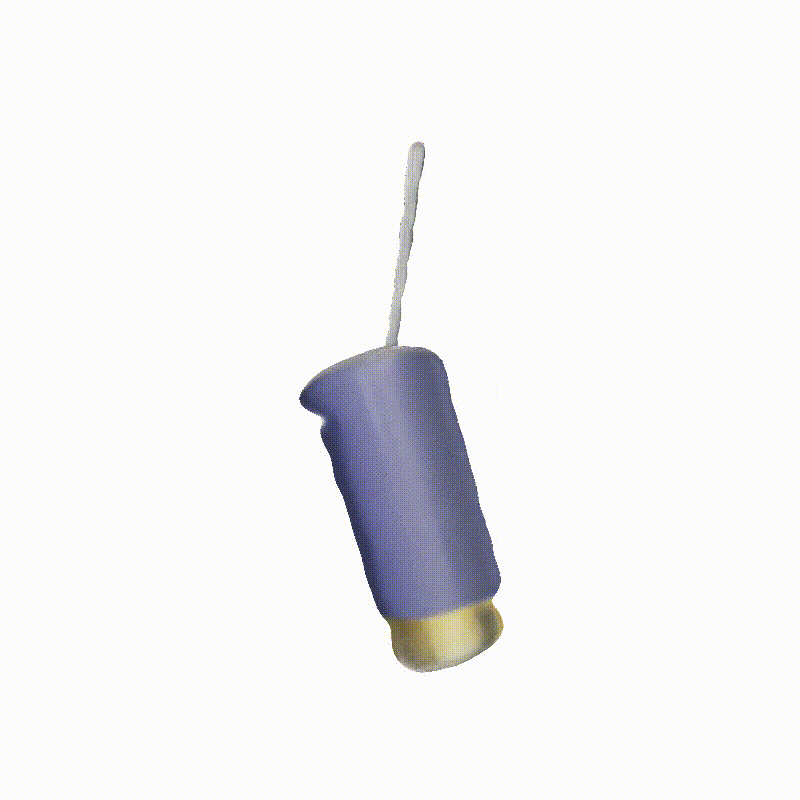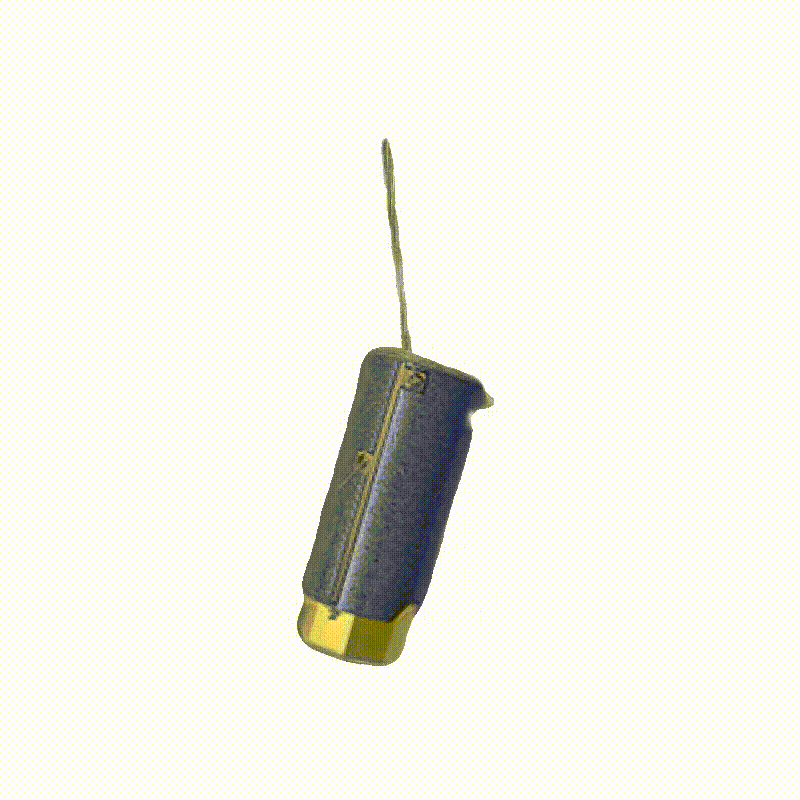
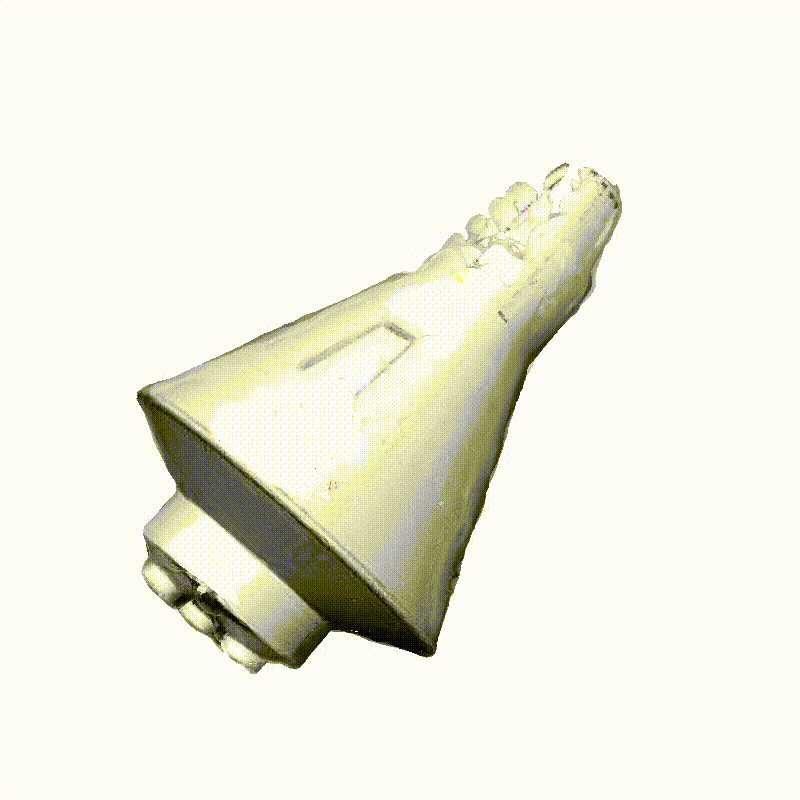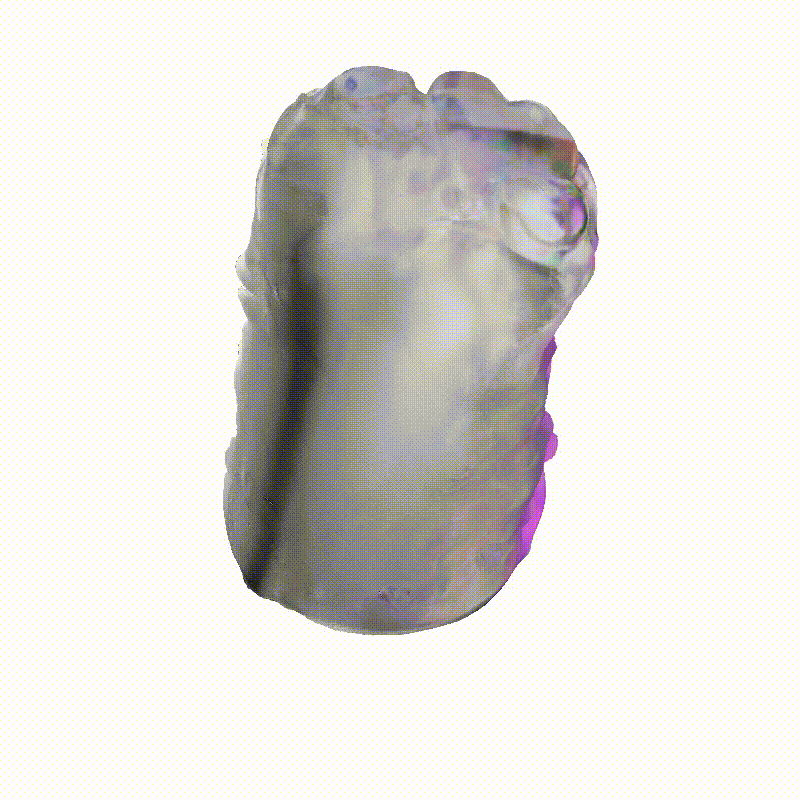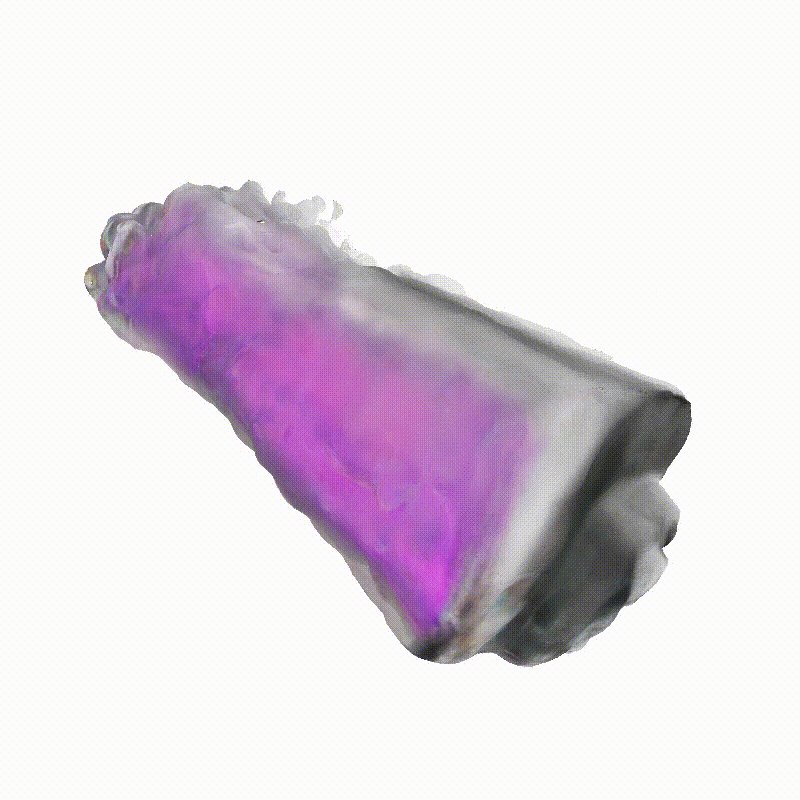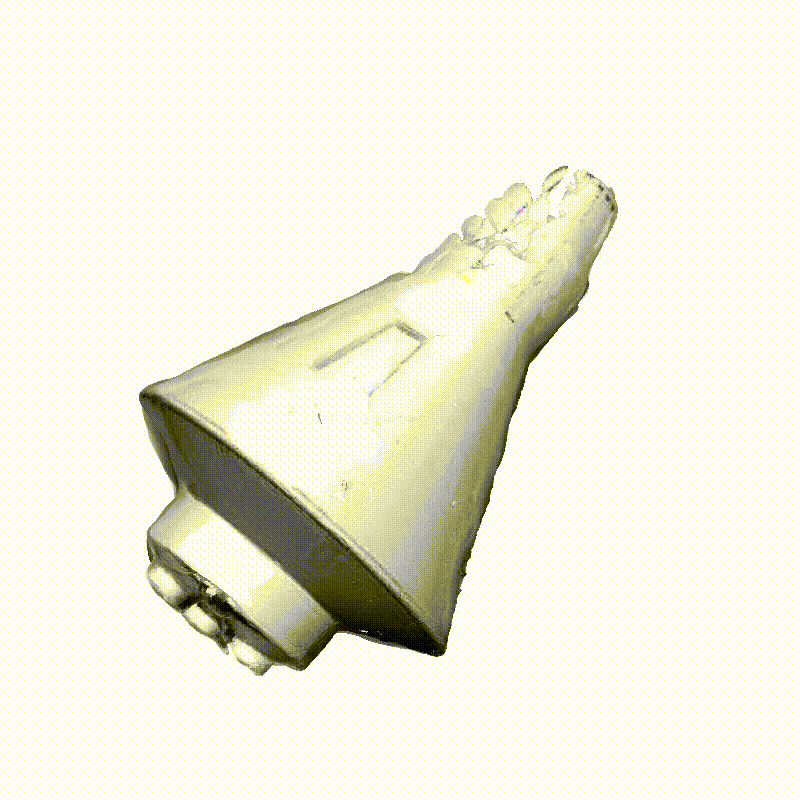
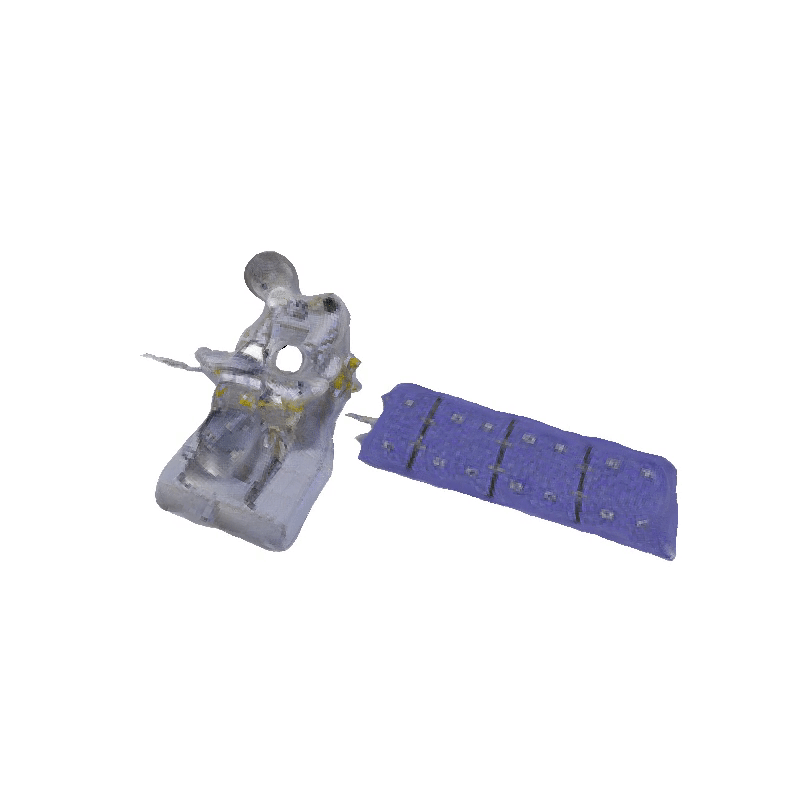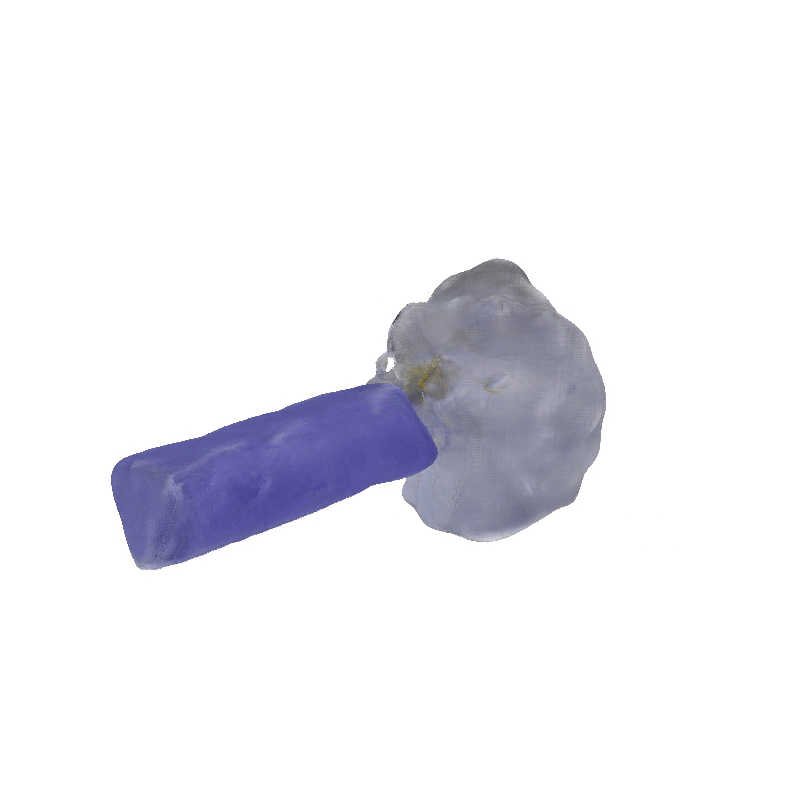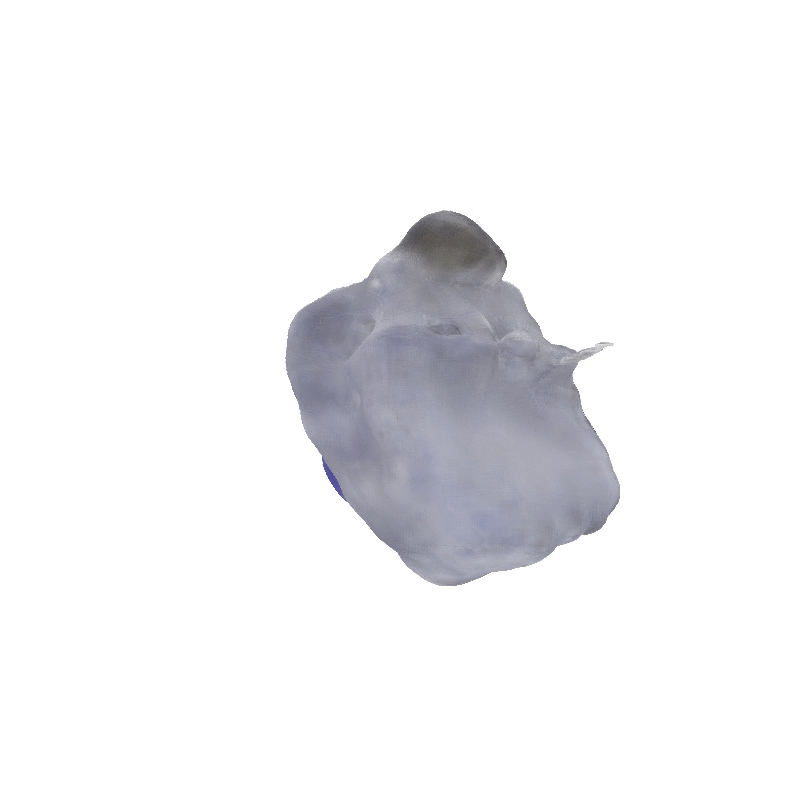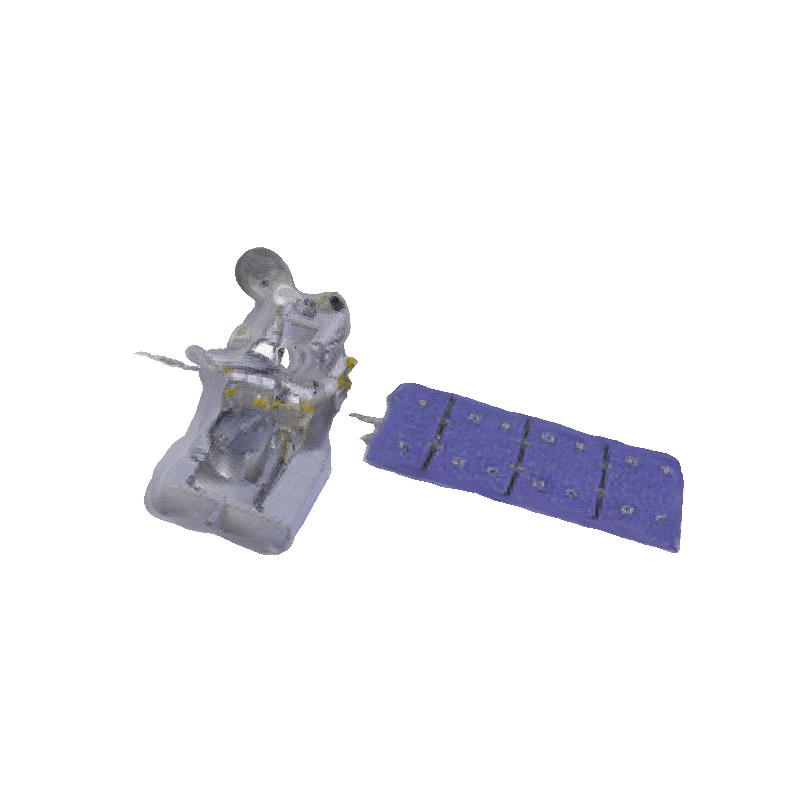
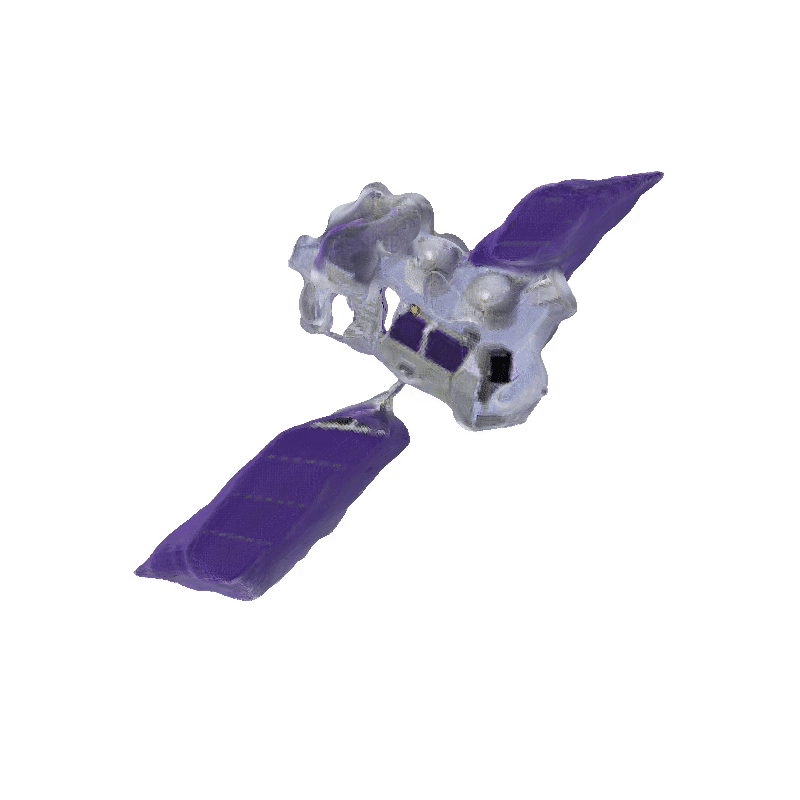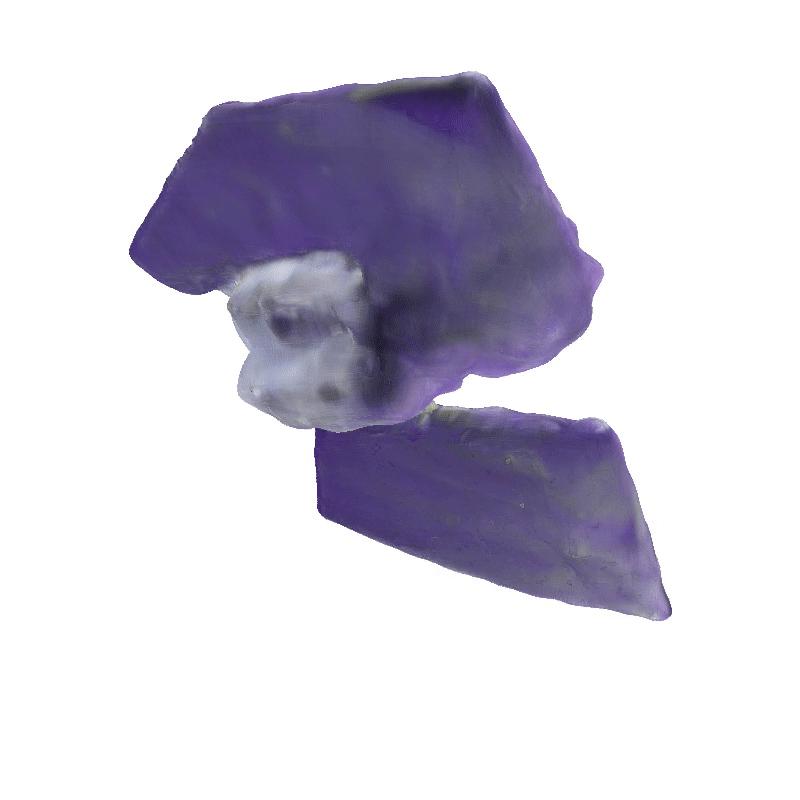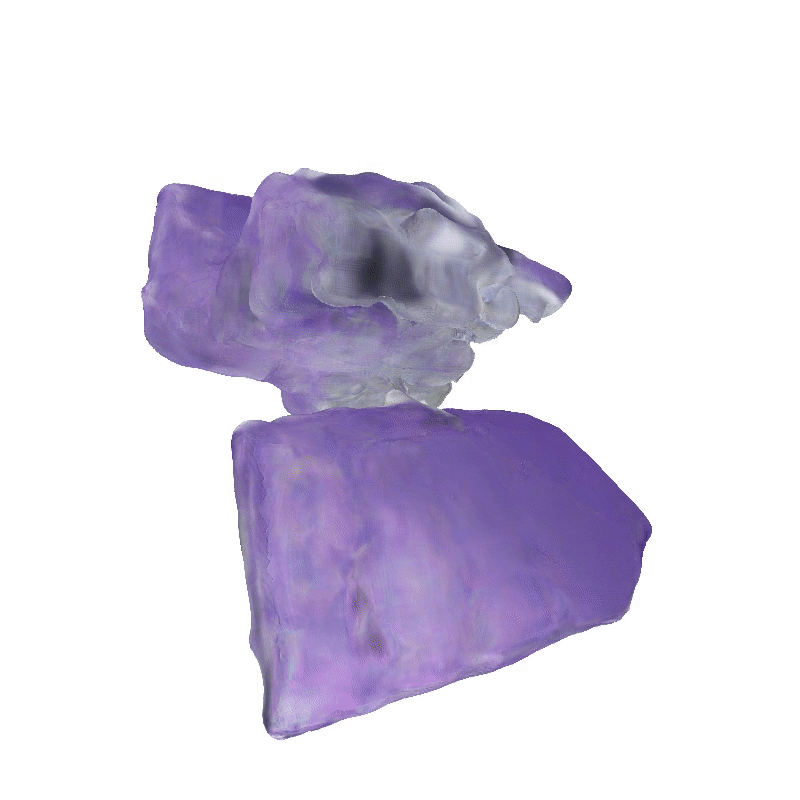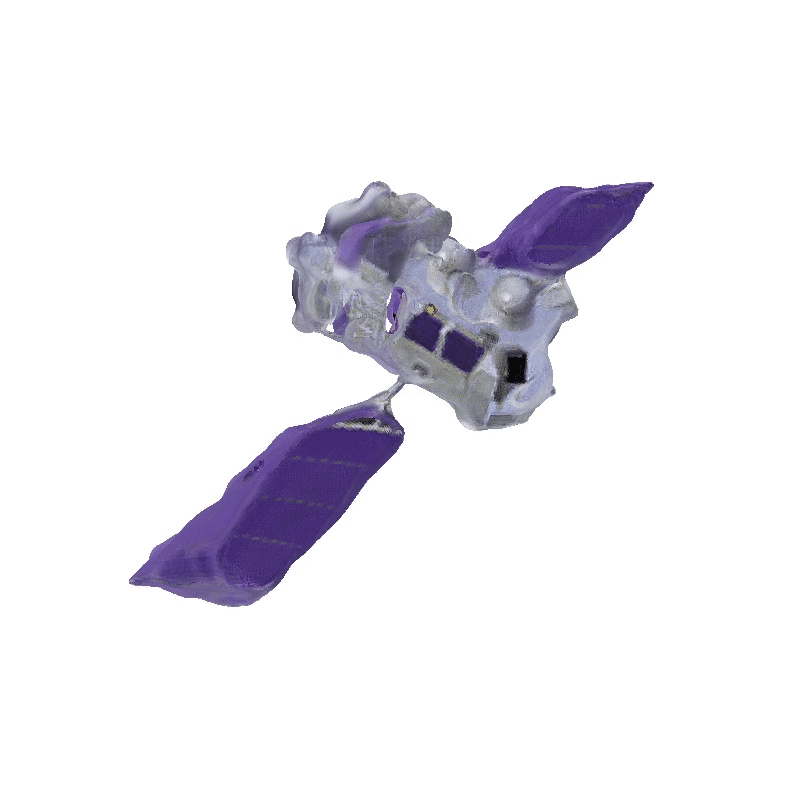
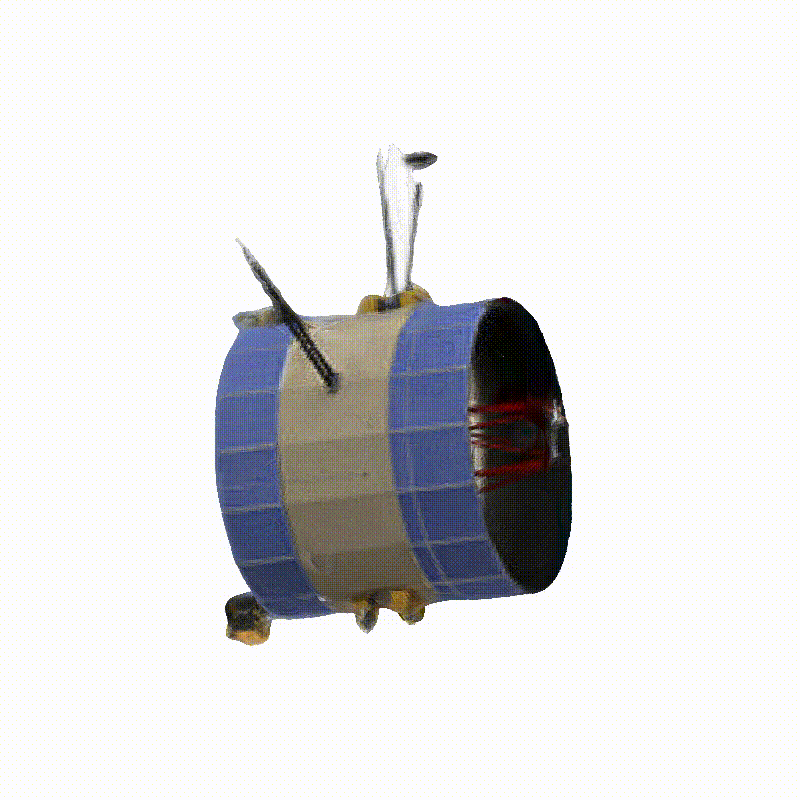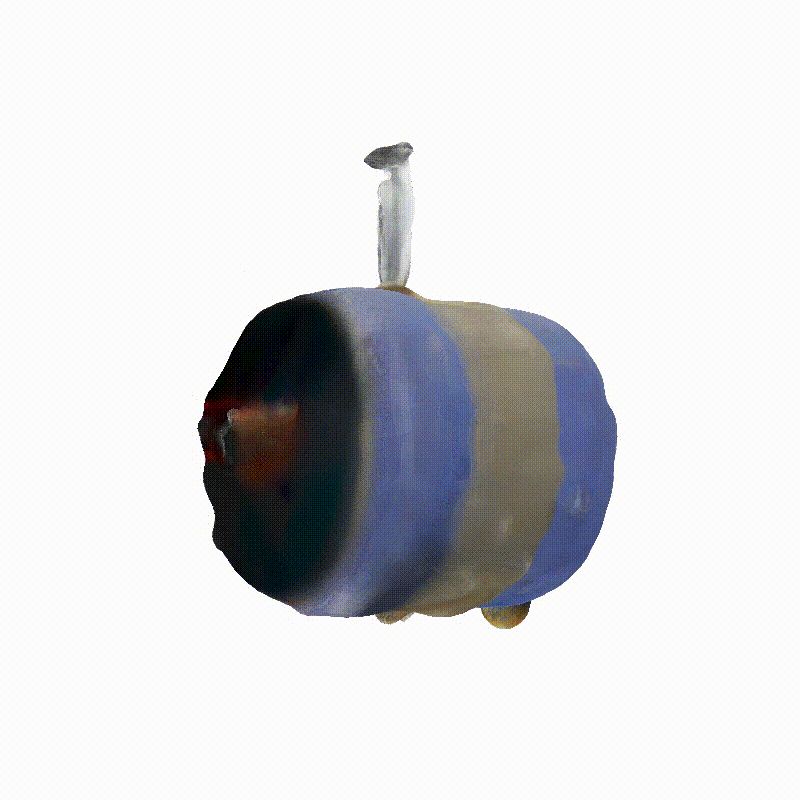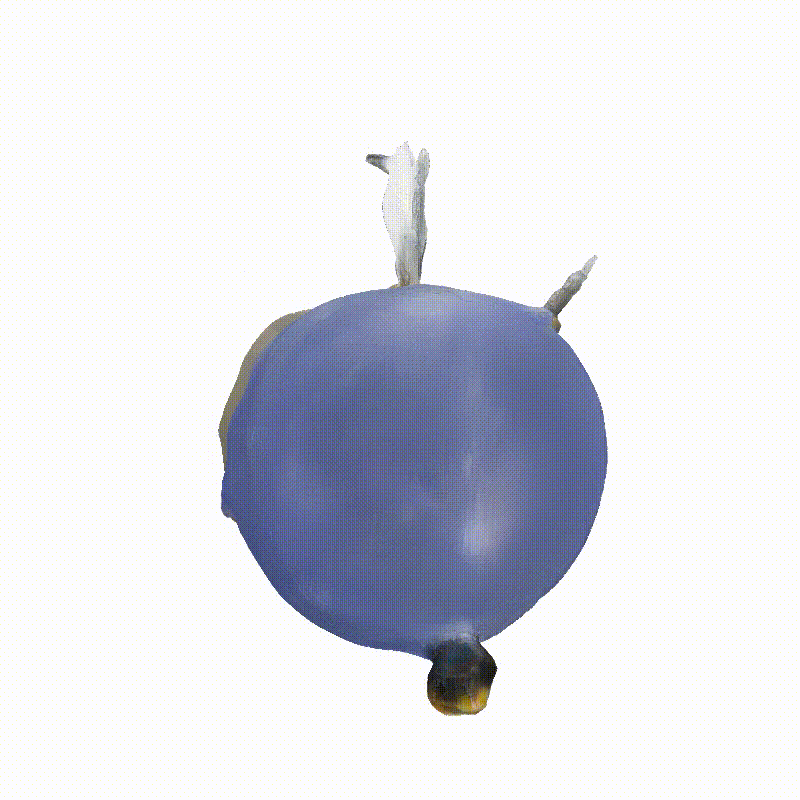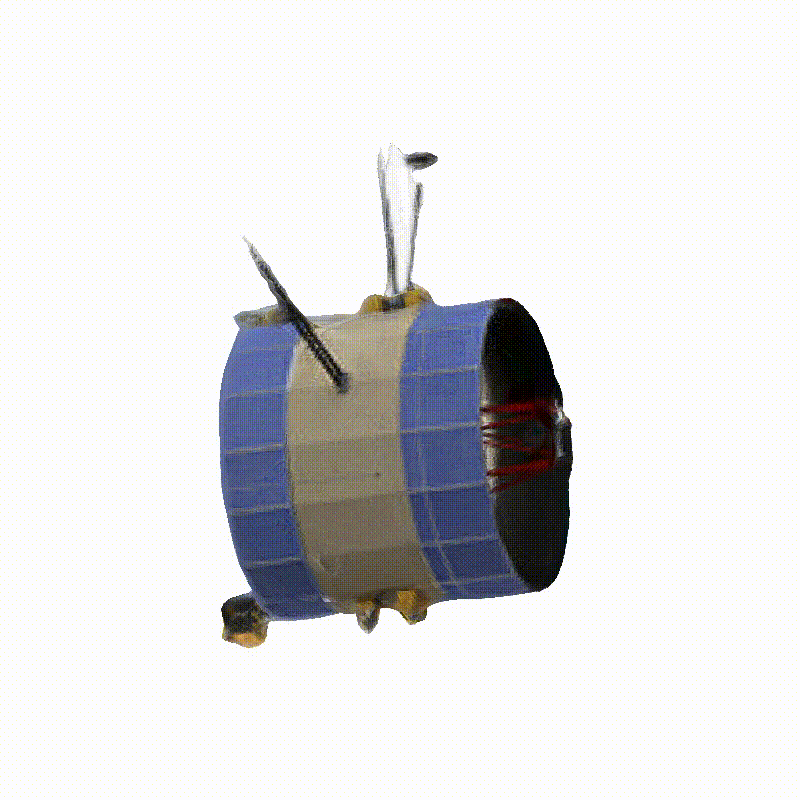
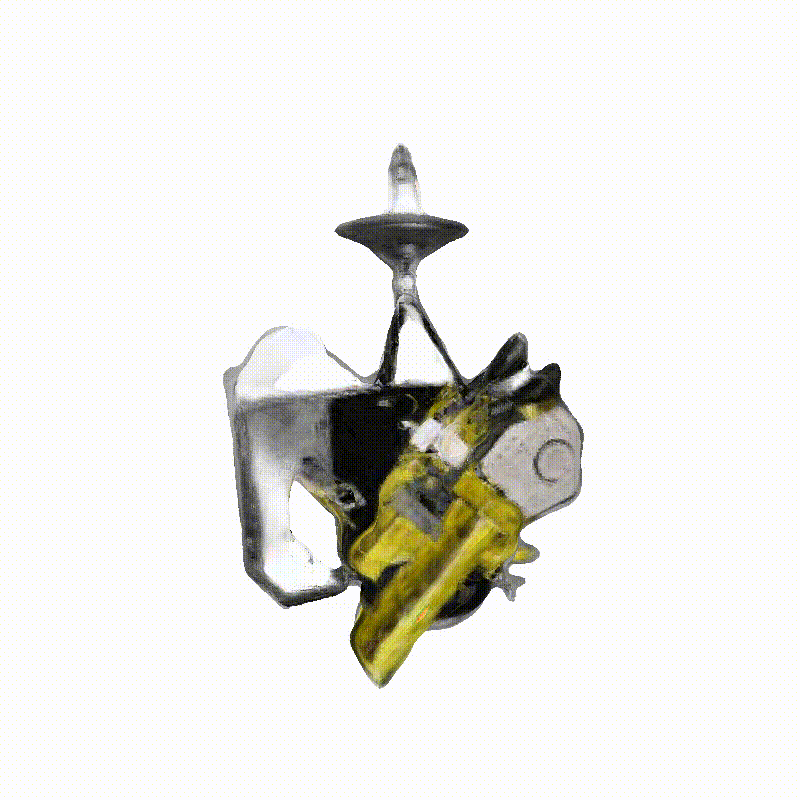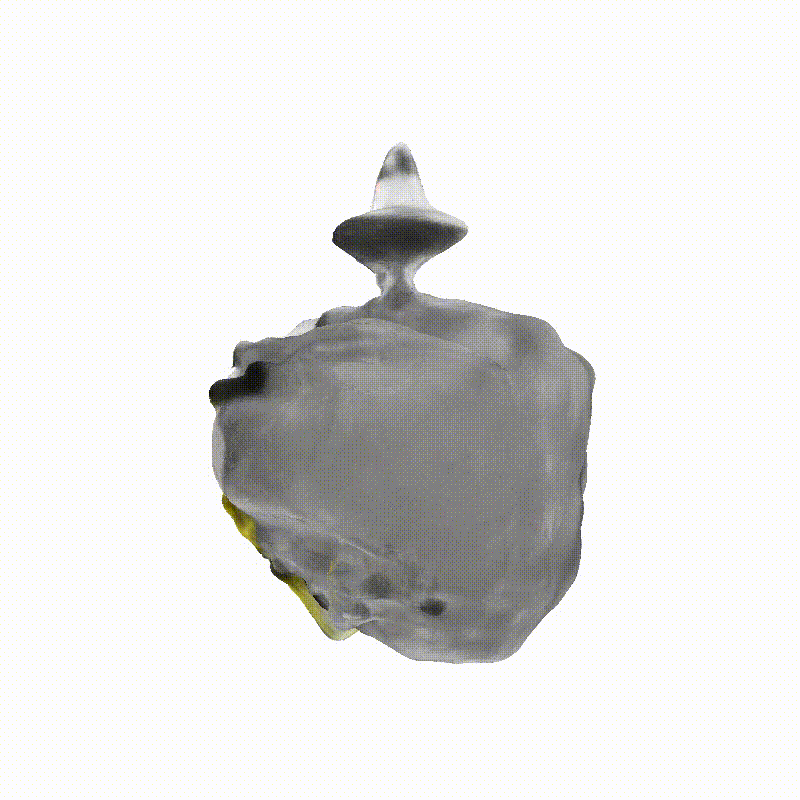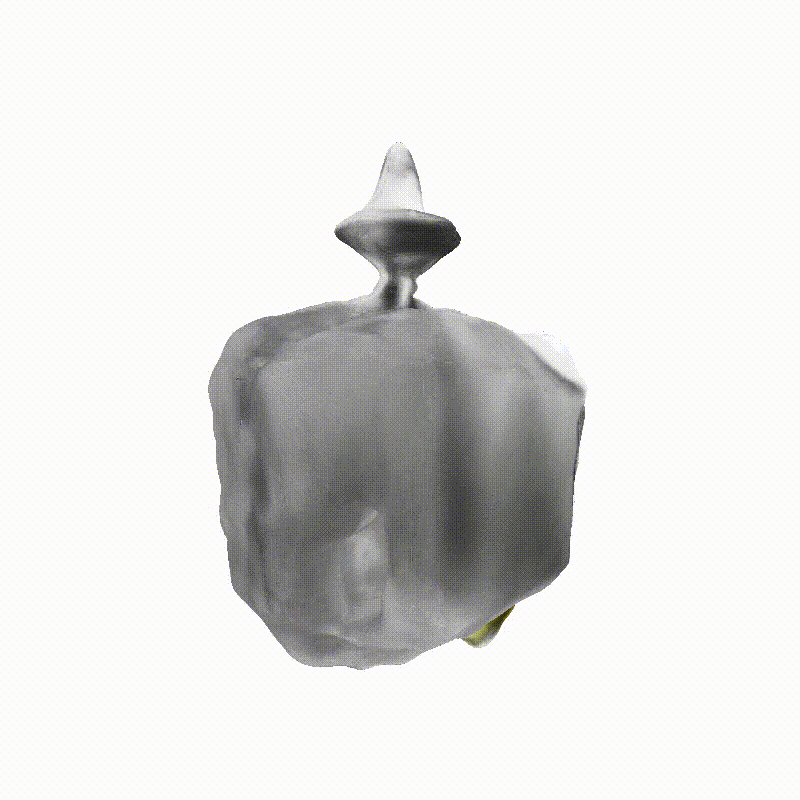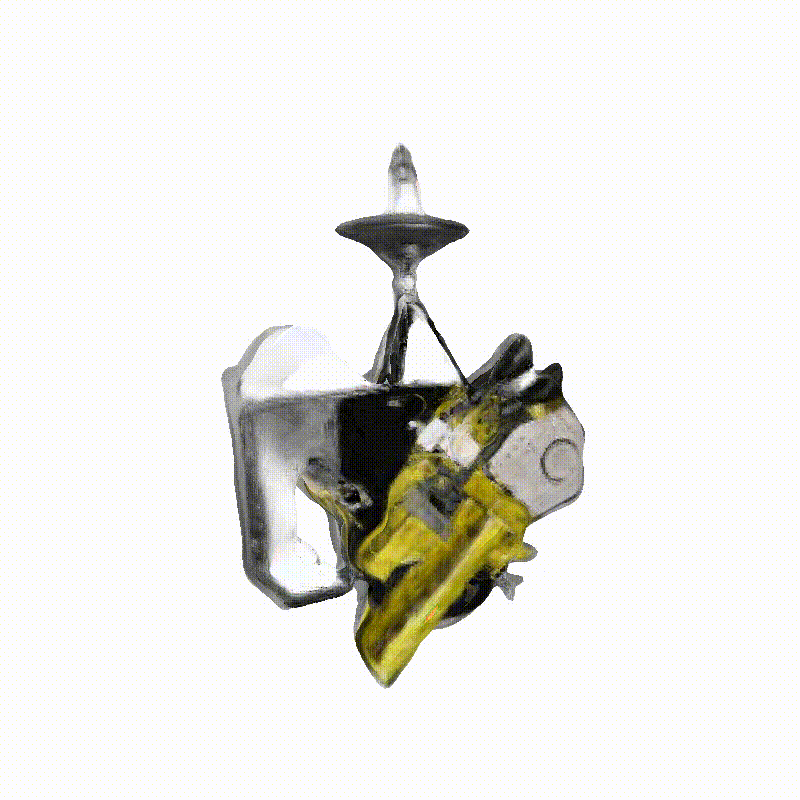
Explorer 1
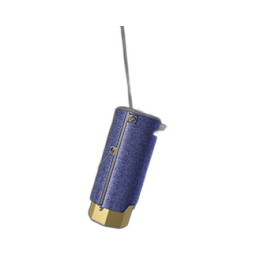
Apollo Lunar Module

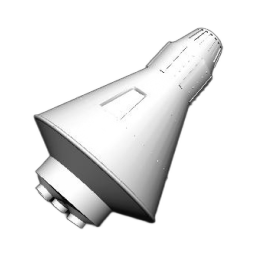
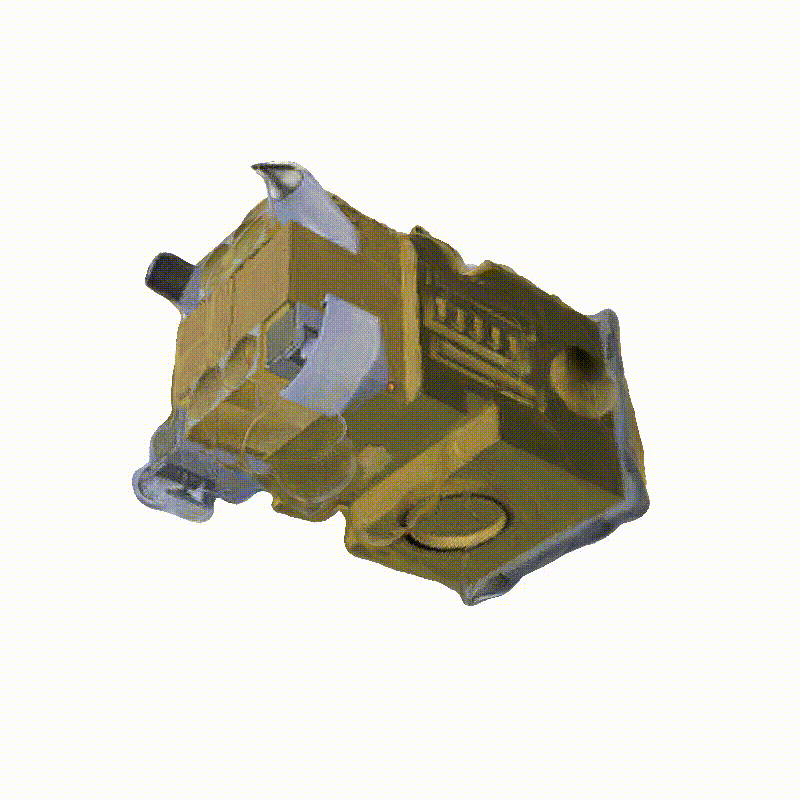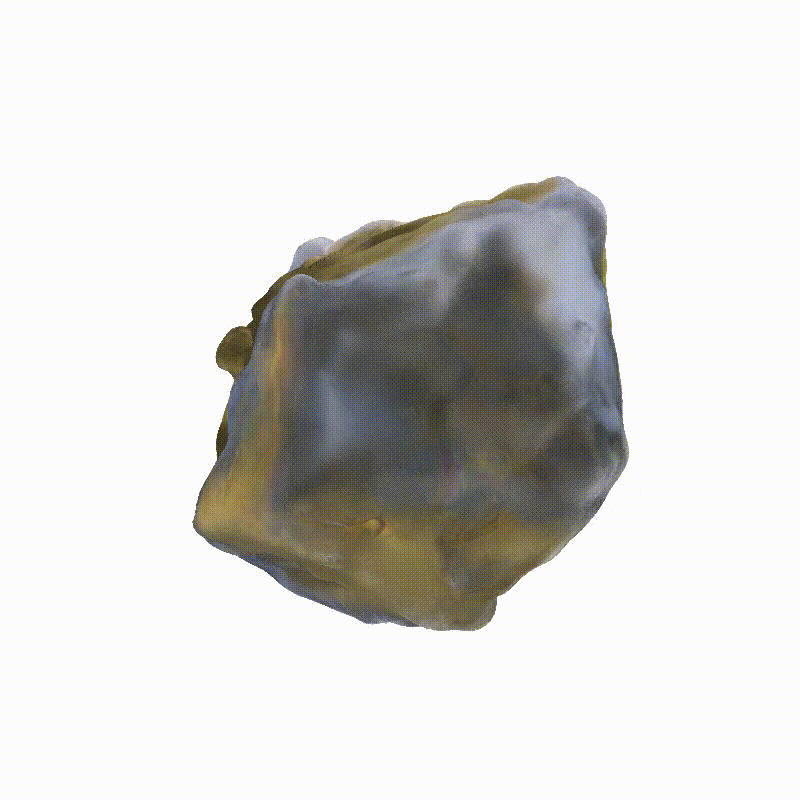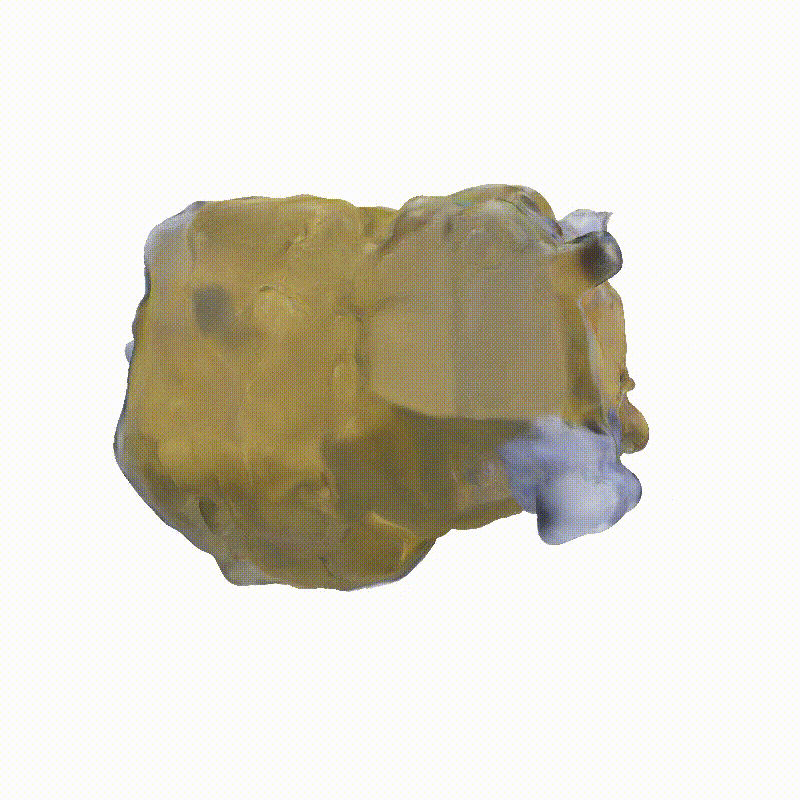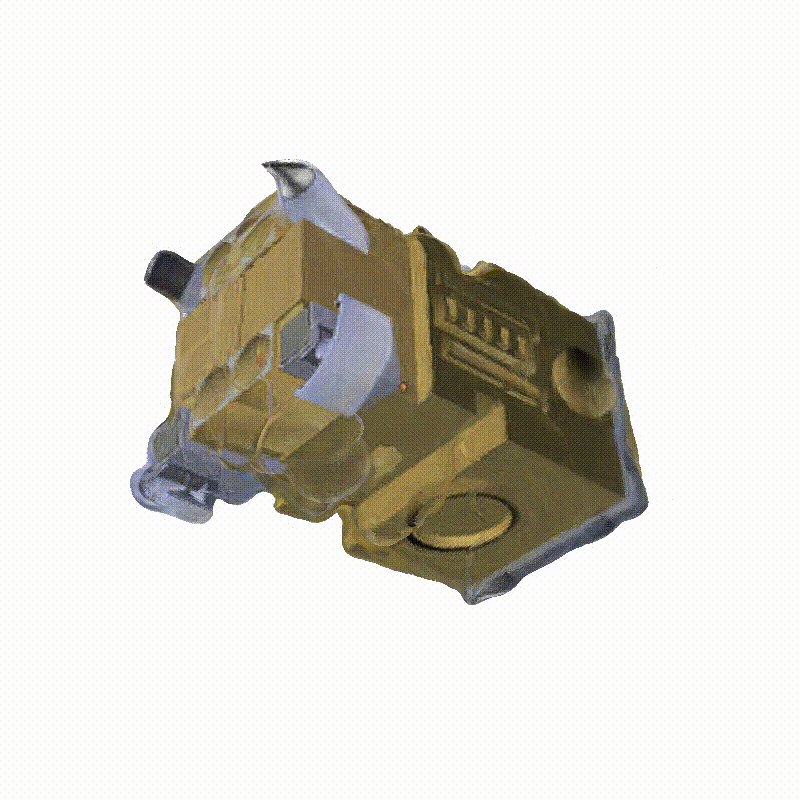
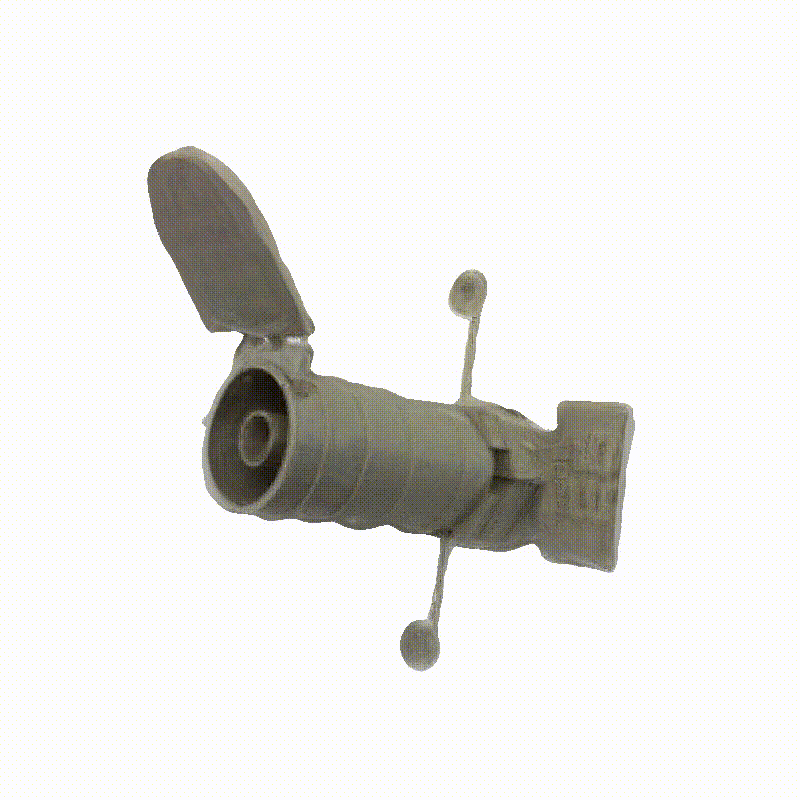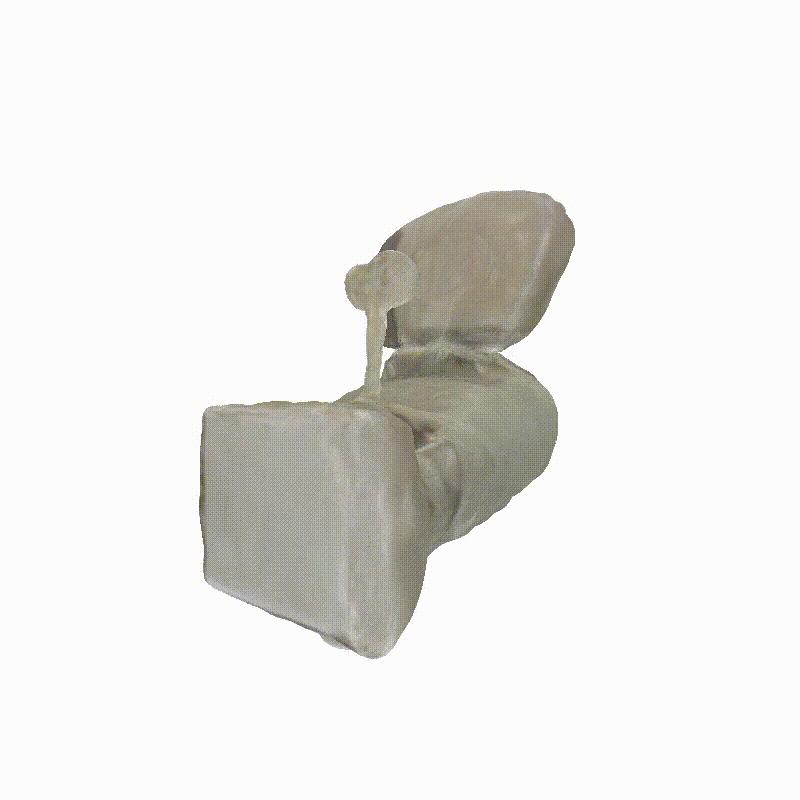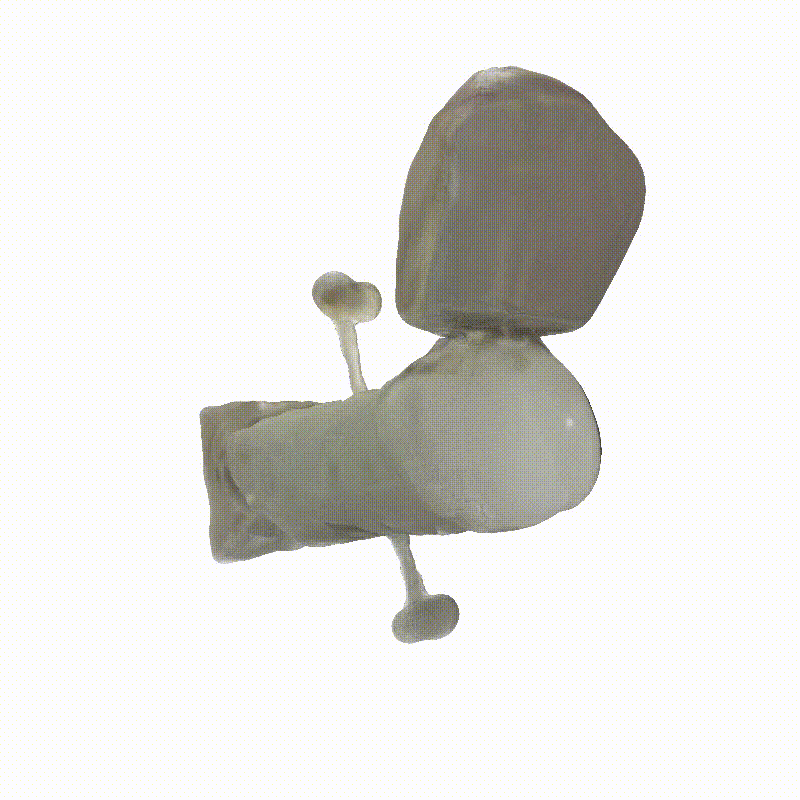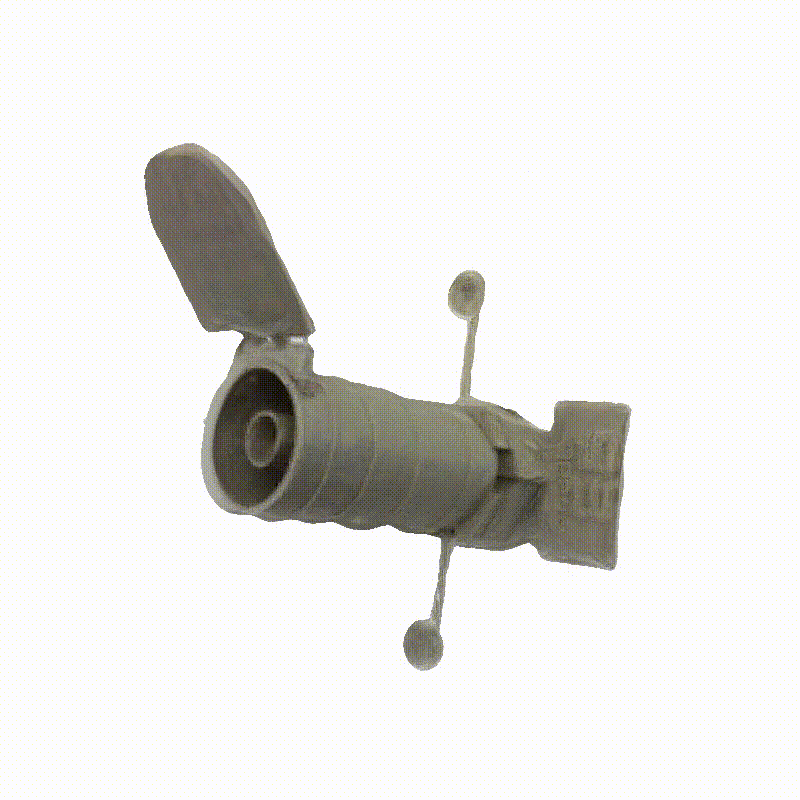
Space Launch System Block 1
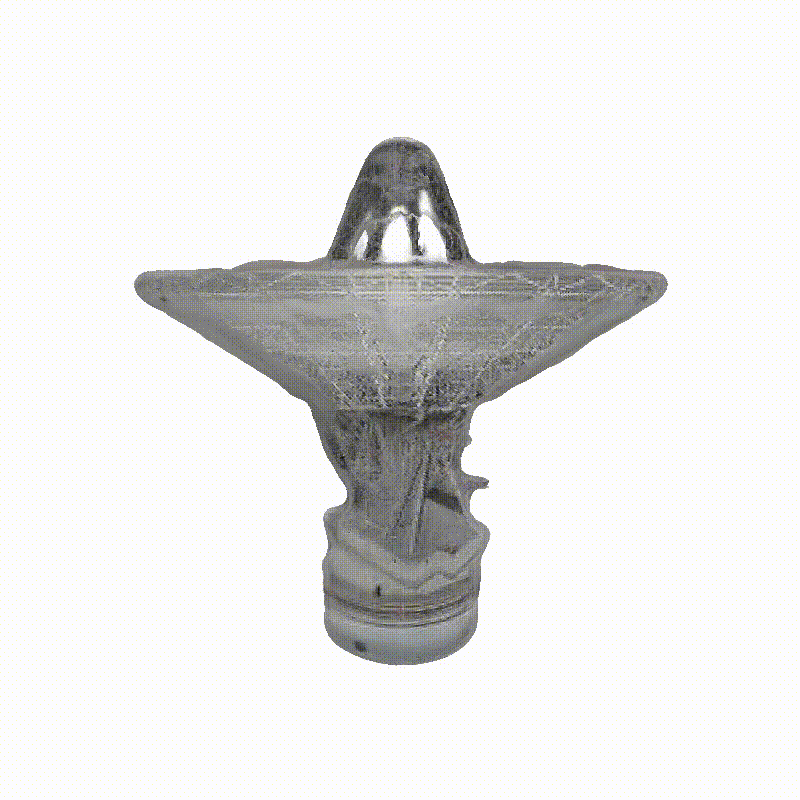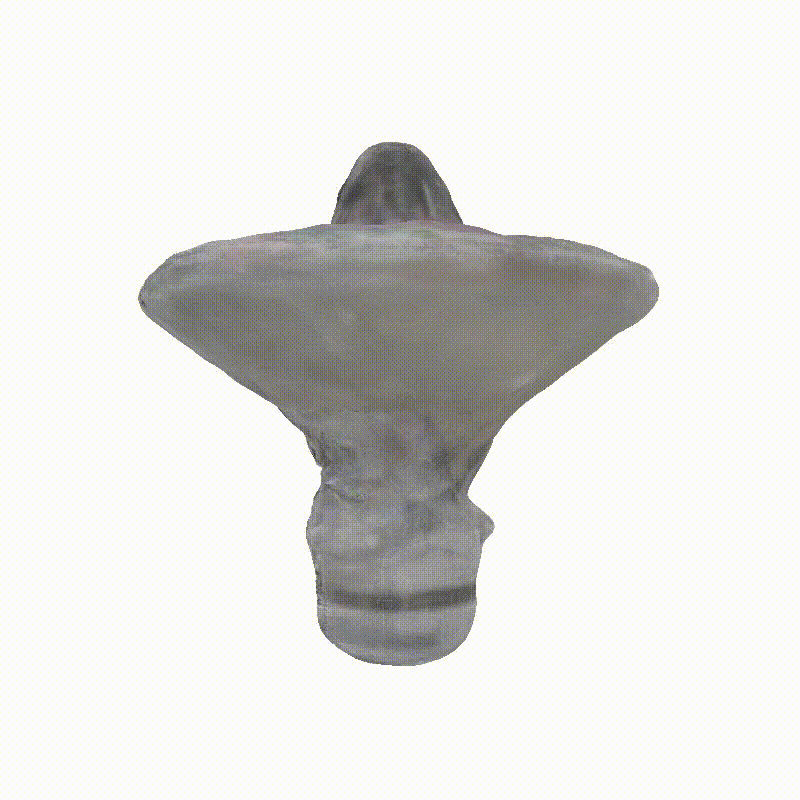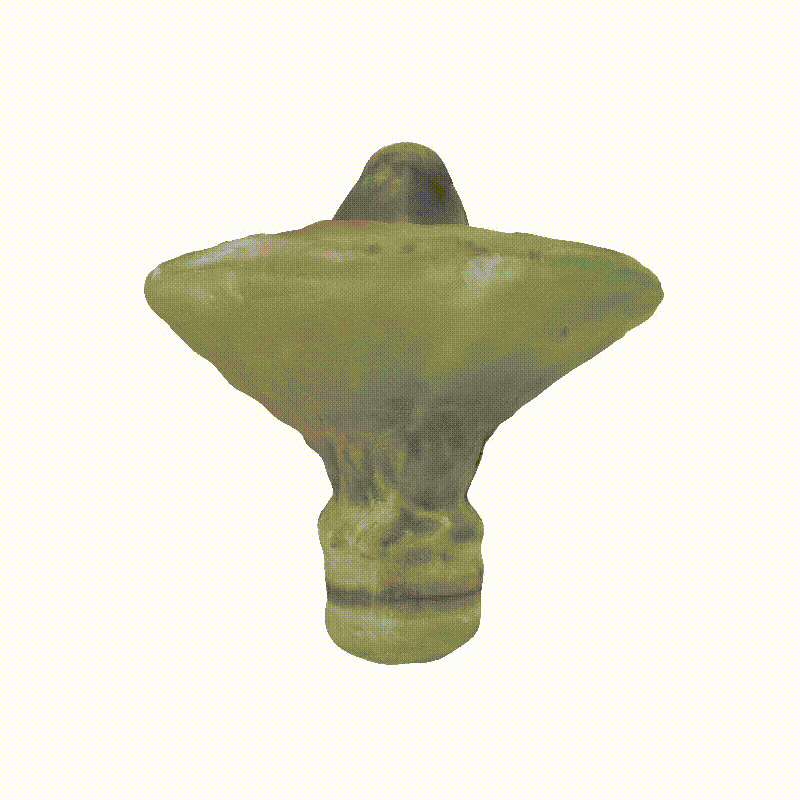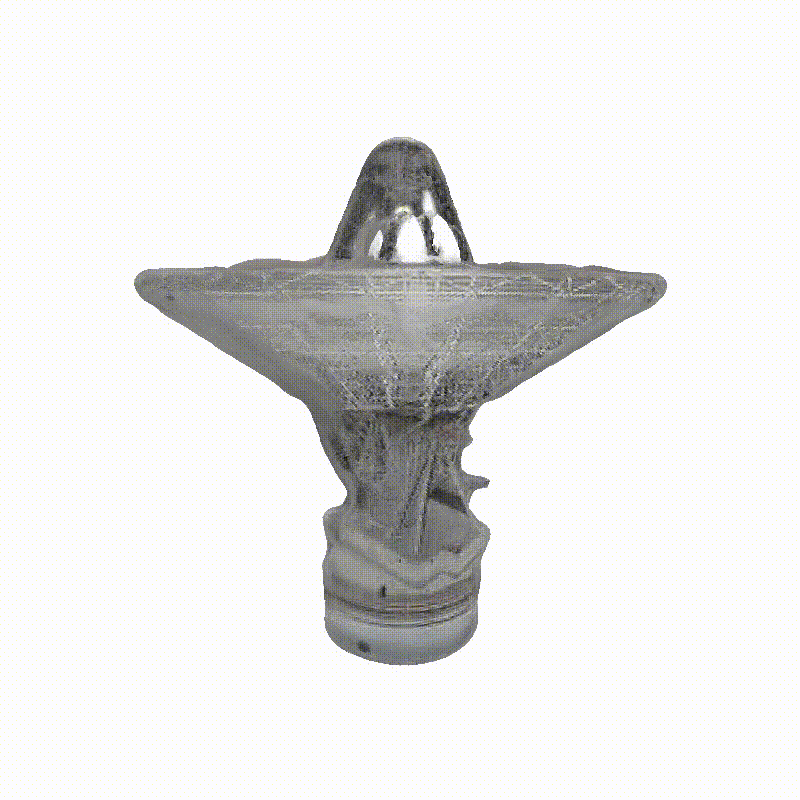
Generated Novel Views

Explorer 1

Apollo Lunar Module

Space Launch System Block 1
3D Meshes
Explorer 1
Apollo Lunar Module
Space Launch System Block 1
Image-to-3D